Stock market indicators are crucial tools that provide insights into the overall health and performance of financial markets. Investors use these indicators to make informed decisions, assess market trends, and formulate investment strategies. Understanding the computation methods and implications of key stock market indicators is essential for navigating the dynamic world of investments.
1. BSE Sensex and NSE Nifty:
Computation:
- BSE Sensex: Computed using the free-float market capitalization of 30 constituent companies, with adjustments for stock splits and corporate actions.
- NSE Nifty: Represents the performance of the 50 largest and most liquid Indian companies, calculated using a free-float market capitalization-weighted methodology.
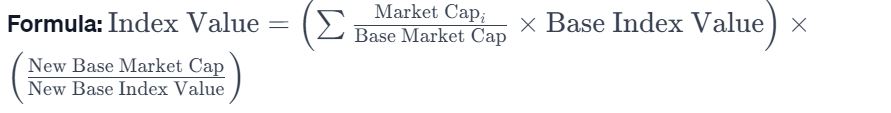
Implications:
- Reflects the overall market sentiment and direction.
- Used by investors, analysts, and policymakers as a benchmark for market performance.
- Influences investment decisions and capital flows.
2. Market Breadth Indicators:
Computation:
- Advance-Decline Ratio: The number of advancing stocks divided by the number of declining stocks.
- Advance-Decline Line (ADL): Cumulative sum of the daily difference between advancing and declining issues.
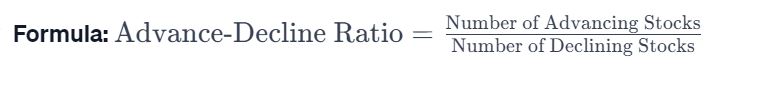

Implications:
- Provides insights into the overall market direction.
- High breadth suggests a broad-based market rally.
- Low breadth may indicate a selective or narrow market movement.
3. Volatility Index (VIX):
Computation:
Measures the market’s expectation of volatility in the near term, calculated based on the weighted prices of Nifty options.
Implications:
- High VIX indicates higher expected market volatility.
- Used for risk assessment and portfolio hedging.
- A low VIX may suggest complacency and potential market stability.
4. Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio:
Computation:
Calculated by dividing the market price per share by the earnings per share (EPS) of a company or an index.
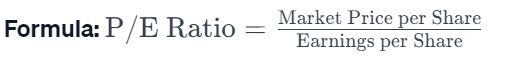
Implications:
- Indicates the valuation of stocks relative to their earnings.
- High P/E ratios may suggest overvaluation, while low ratios may indicate undervaluation.
- Helps investors make informed decisions on stock investments.
5. Moving Averages:
Computation:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Calculated by averaging closing prices over a specific time period.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Gives more weight to recent prices, providing a more responsive indicator.
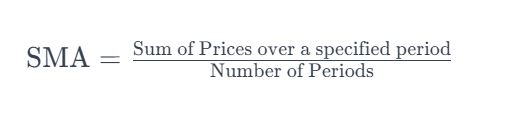
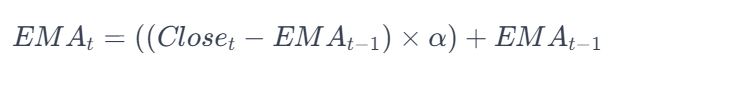
Implications:
- Identifies trends and potential trend reversals.
- Used for technical analysis and timing entry/exit points.
- Popular timeframes include 50-day, 100-day, and 200-day moving averages.
6. Relative Strength Index (RSI):
Computation:
Measures the speed and change of price movements, calculated based on the average of upward and downward price changes over a specified period.
Implications:
- Indicates overbought or oversold conditions.
- Used for identifying potential trend reversals.
- Provides insights into the strength of a stock’s recent price movements.
7. Dividend Yield:
Computation:
Calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share by the market price per share.

Implications:
- Reflects the return on investment through dividends.
- Higher dividend yields may attract income-focused investors.
- Provides insights into the financial health and dividend policies of companies.
8. Foreign Institutional Investment (FII) and Domestic Institutional Investment (DII) Activity:
Computation:
Represents the net investments made by foreign and domestic institutional investors in the stock market.
Implications:
- Reflects investor confidence in the Indian market.
- Significant FII inflows may indicate positive sentiment.
- DII activity reflects local investor participation and market resilience.
Conclusion:
Stock market indicators in India are diverse, offering a multifaceted view of market conditions. Investors, analysts, and policymakers leverage these indicators to make informed decisions, manage risks, and gauge overall market health. Understanding the computation methods and implications of these indicators is crucial for navigating the dynamic landscape of the Indian stock market and optimizing investment strategies.




