The Put-Call Parity Principle is a fundamental concept in options trading that establishes a relationship between the prices of European call and put options of the same class, with the same strike prices and expiration dates. This principle helps maintain equilibrium in the options market, allowing traders to identify and capitalize on arbitrage opportunities. Let’s delve into the intricacies of the Put-Call Parity Principle.
Put-Call Parity Formula:
The Put-Call Parity Principle is expressed through the following formula:
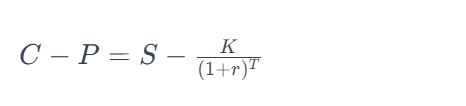
Where:
- C is the price of the European call option.
- P is the price of the European put option.
- S is the current stock price.
- K is the strike price of the options.
- r is the risk-free interest rate.
- T is the time to expiration.
Understanding the Put-Call Parity Principle:
- Equilibrium Relationship: The principle suggests that at any given time, the difference between the price of a European call option and a European put option with the same strike price and expiration date should be equal to the difference between the current stock price and the present value of the strike price.
- Arbitrage Opportunities: If there is a deviation from the parity relationship, it creates an arbitrage opportunity. Traders can exploit these mispricing’s to make risk-free profits.
- Call and Put Options Dynamics: The principle highlights the symmetrical nature of call and put options in terms of their pricing and their relationship to the underlying stock.
Practical Application:
- Arbitrage Scenarios: Traders actively monitor options prices and underlying stock values to identify situations where the Put-Call Parity is not upheld. They then execute trades to capitalize on the temporary mispricing.
- Risk-Free Profit Opportunities: By engaging in simultaneous buy and sell transactions involving options and the underlying stock, traders can create portfolios that result in risk-free profits until the parity relationship is restored.
Considerations in Options Trading:
- Assumptions and Limitations: The Put-Call Parity Principle is based on certain assumptions, including frictionless markets and no transaction costs. Real-world deviations may occur.
- American vs. European Options: The principle primarily applies to European options due to their specific exercise characteristics. American options, which can be exercised before expiration, introduce additional complexities.
Conclusion:
The Put-Call Parity Principle is a cornerstone in options trading, providing a framework for understanding the interconnectedness of call and put option prices. Traders and investors can leverage this principle to detect and exploit mispricing’s, contributing to the efficient functioning of the options market. Understanding the equilibrium established by the Put-Call Parity is essential for those seeking to navigate the intricate landscape of options trading.



